Problem #DES-pythag
Problem
Today we will focus on applications of the Pythagorean theorem in geometry and number theory. This famous and ancient theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the area of a square on a hypothenuse (the longest side) is the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. \[a^2 + b^2 = c^2\]
There are over a 100 proofs of Pythagorean theorem, a quite simple one is visible below:
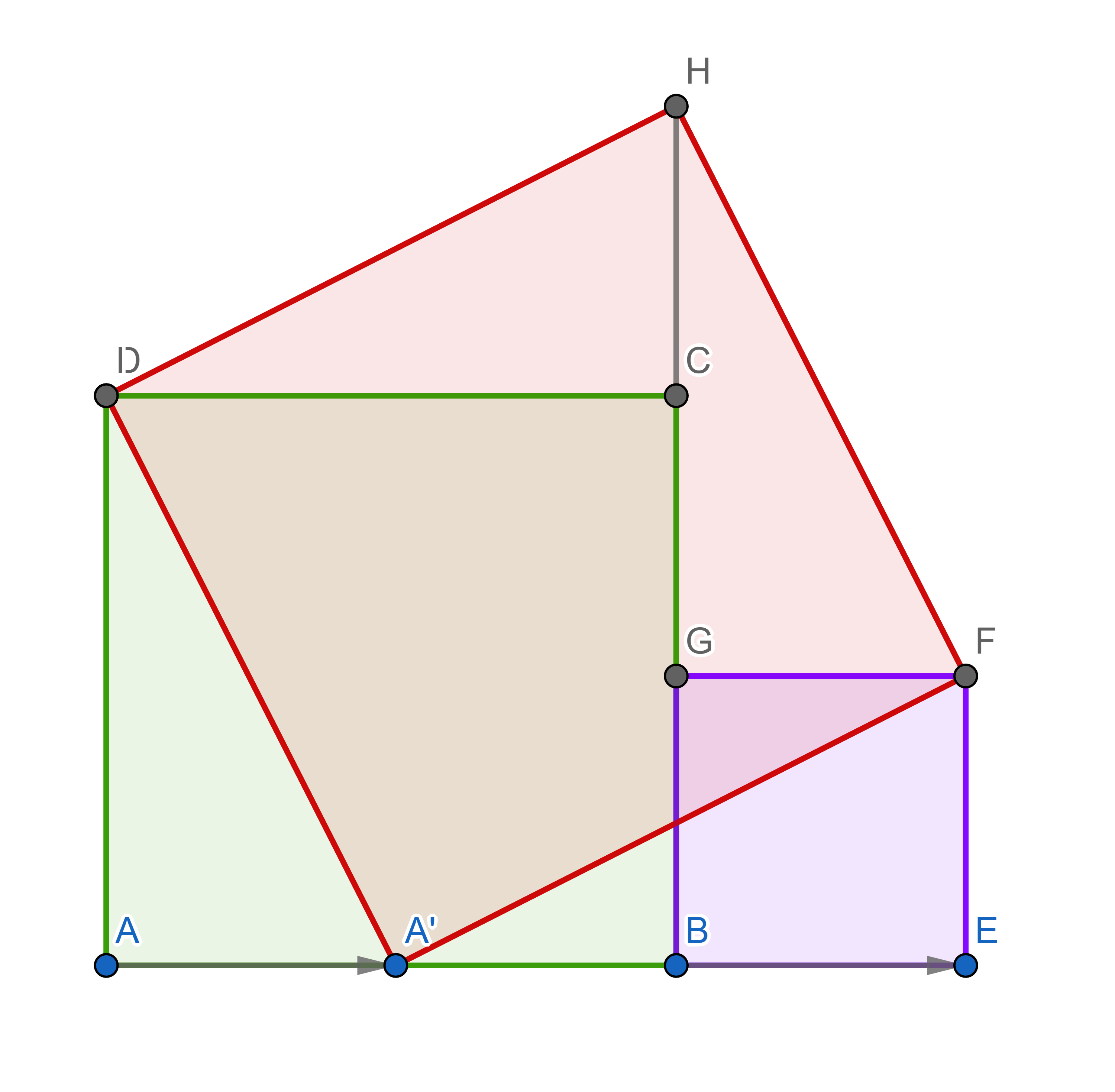
Four right triangles in this picture are identical (congruent): \(\triangle A A' D, \triangle EFA', \triangle GFH\) and \(\triangle CHD\). By moving the triangles around you can see that the large red square has the same area as the sum of areas of the other two squares (violet and green).
Today’s session is not only about geometry, we will also learn something about the equation \(a^2 + b^2 = c^2\), where all the numbers \(a,b,c\) are integers.