After login you will be able to create your own lists of problems.
Problems
Found: 2
Cut a square into five triangles in such a way that the area of one of these triangles is equal to the sum of the area of other four triangles.
The Pythagorean Theorem is one of the most important facts about geometry. It says that if we have a right-angled triangle (i.e: it has an angle of \(90^\circ\)), whose longest side measures \(C\), and its other two other sides measure \(A\) and \(B\):
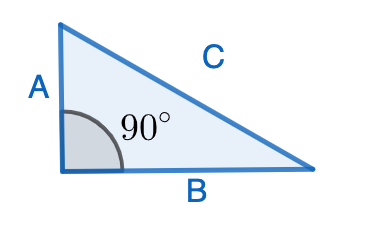
then \(A^2+B^2=C^2\). There are many proofs of this fact, and some involve dissections! Let’s have a look at the following two ways to dissect the same square:
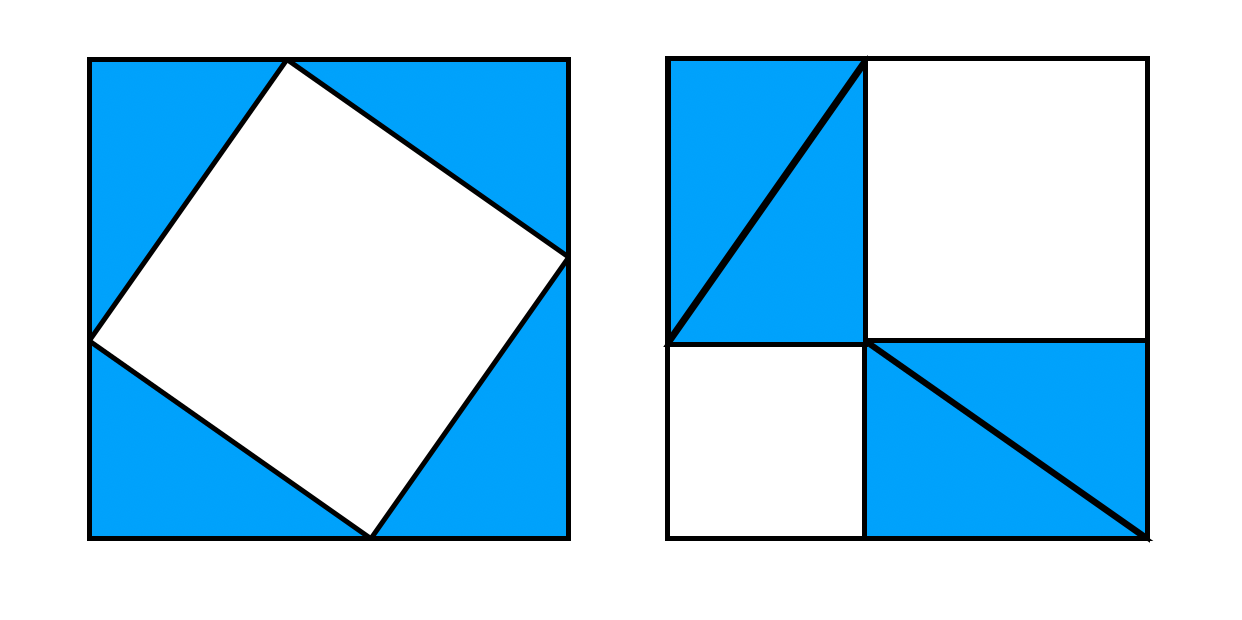
Can you explain how these dissections prove the Pythagorean Theorem?