Problems
Find the mistake in the sequence of equalities: \(-1=(-1)^{\frac{2}{2}}=((-1)^2)^{\frac{1}{2}}=1^{\frac{1}{2}}=1\).
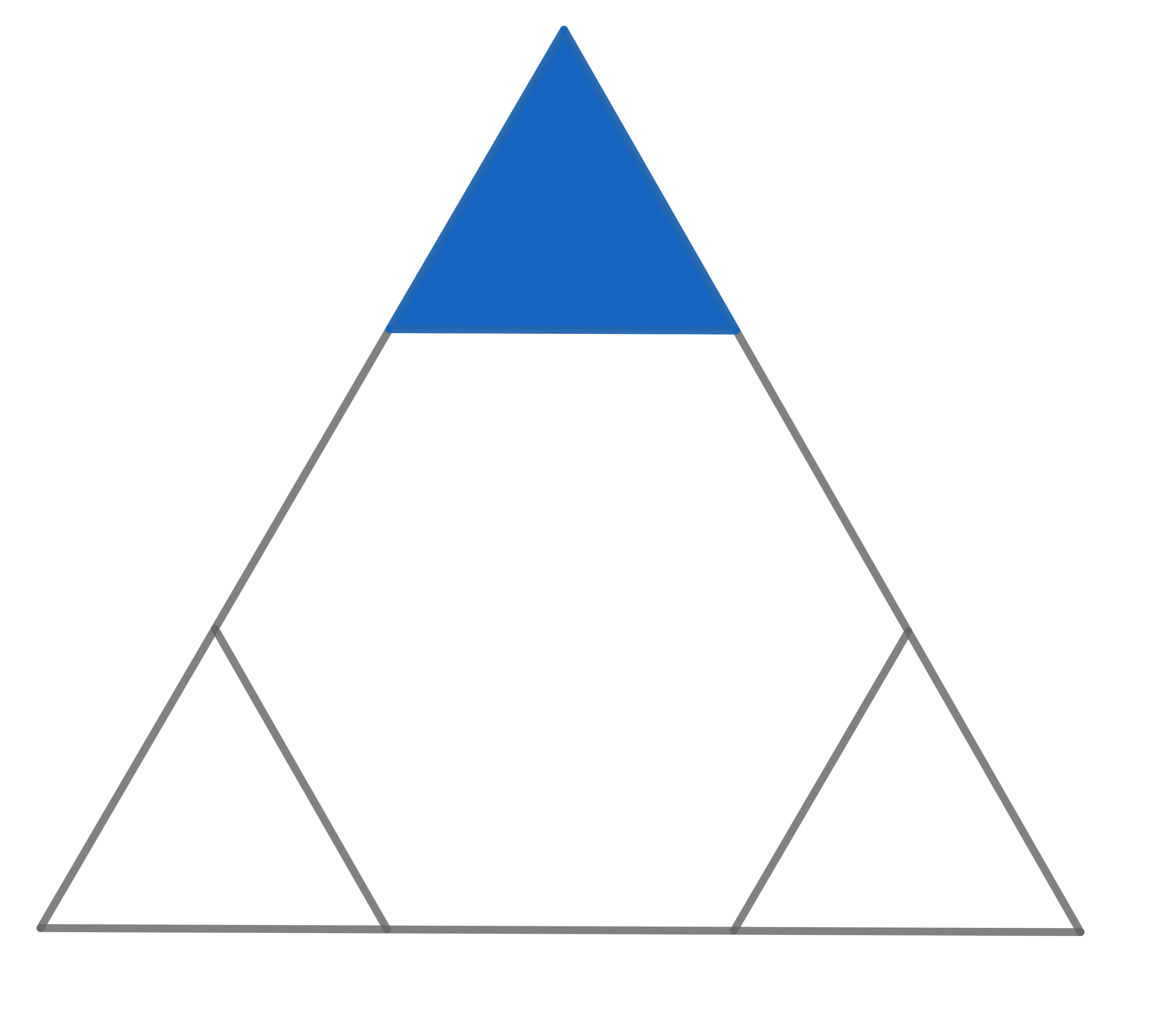
The triangle visible in the picture is equilateral. The hexagon inside is a regular hexagon. If the area of the whole big triangle is \(18\), find the area of the small blue triangle.
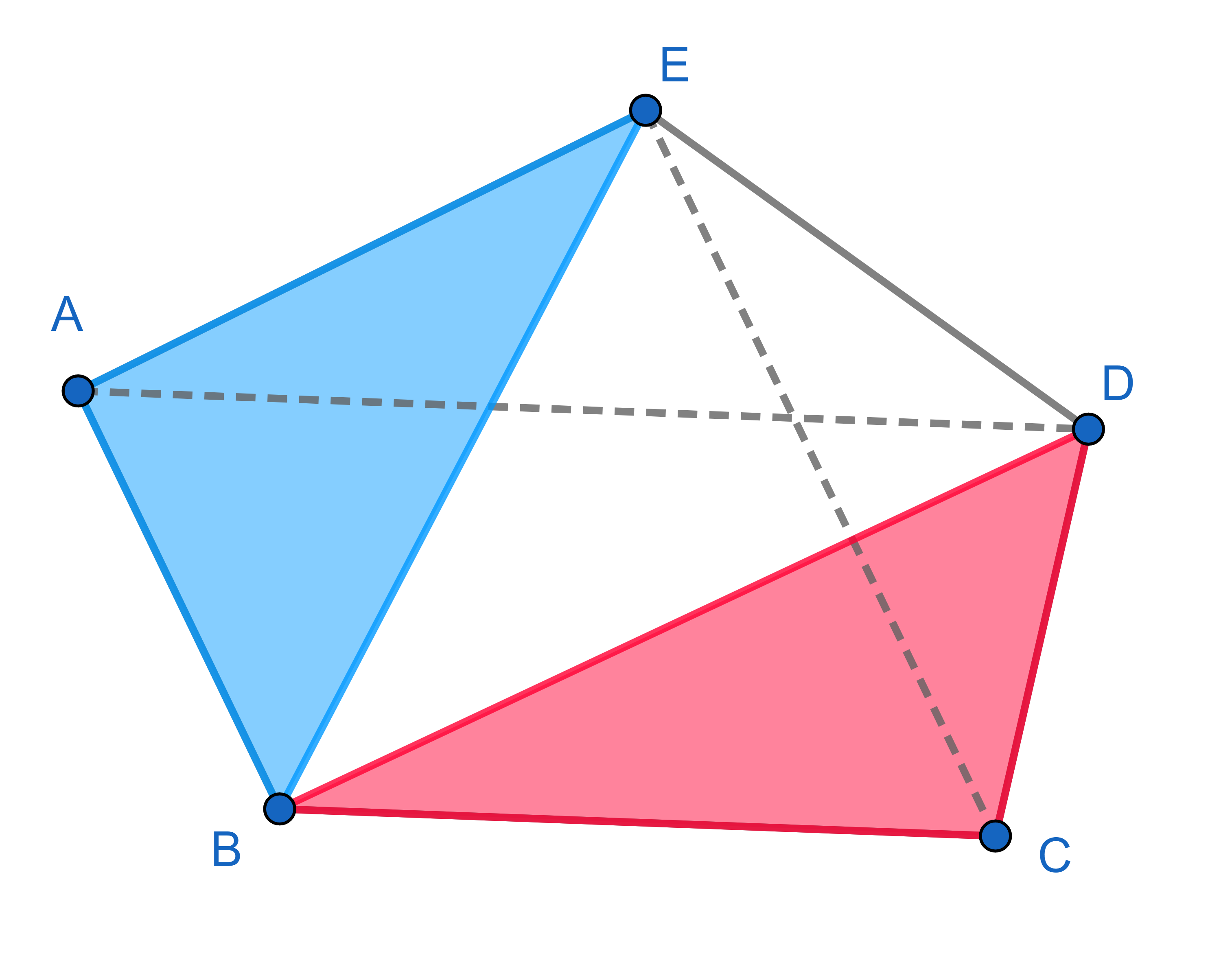
In a pentagon \(ABCDE\), diagonal \(AD\) is parallel to the side \(BC\) and the diagonal \(CE\) is parallel to the side \(AB\). Show that the areas of the triangles \(\triangle ABE\) and \(\triangle BCD\) are the same.
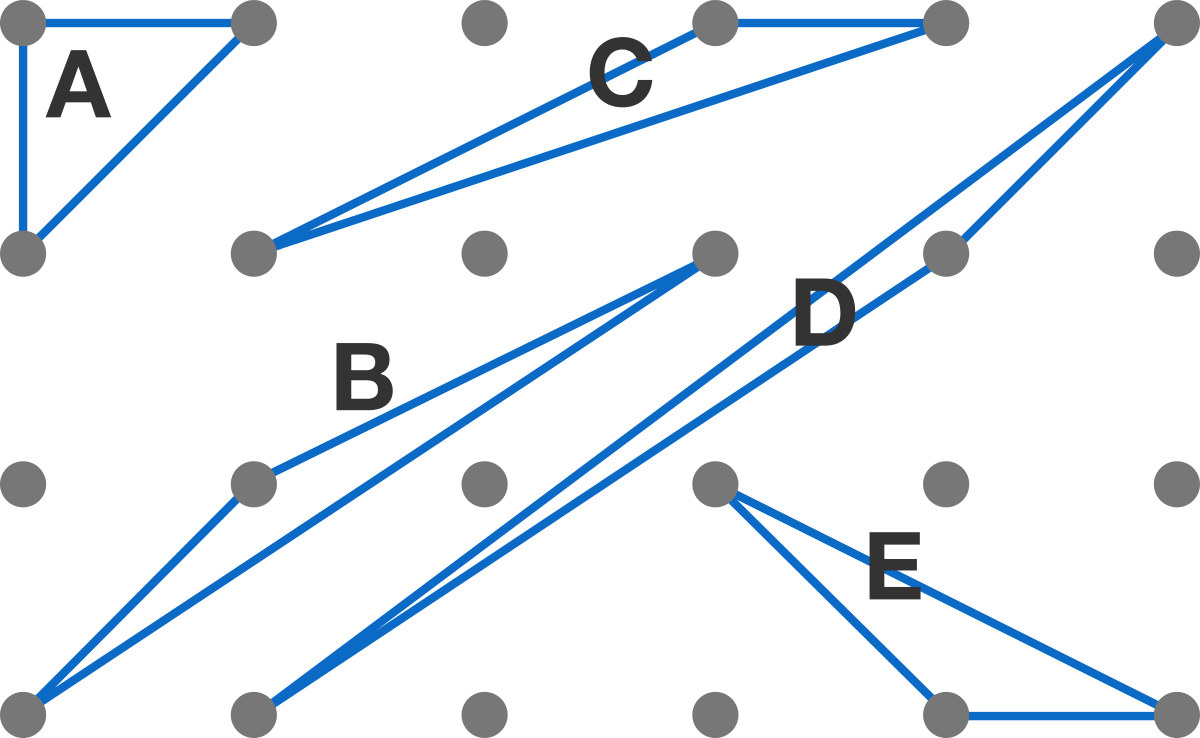
Which triangle has the largest area? The dots form a regular grid.
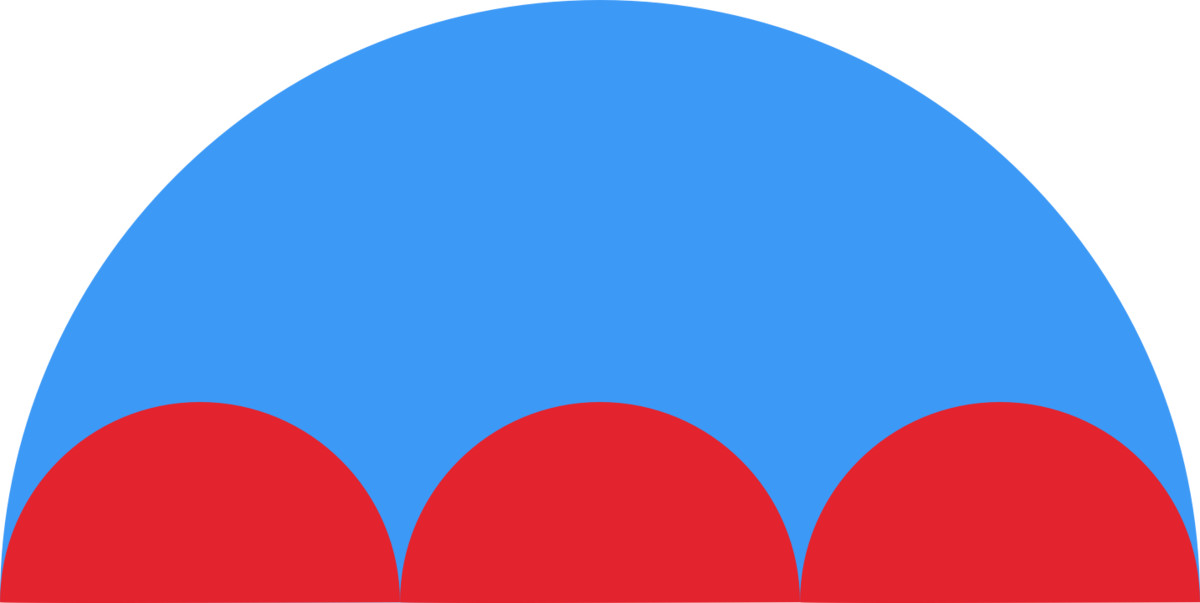
What is the ratio between the red and blue area? All shapes are semicircles and the red ones have equal radii.
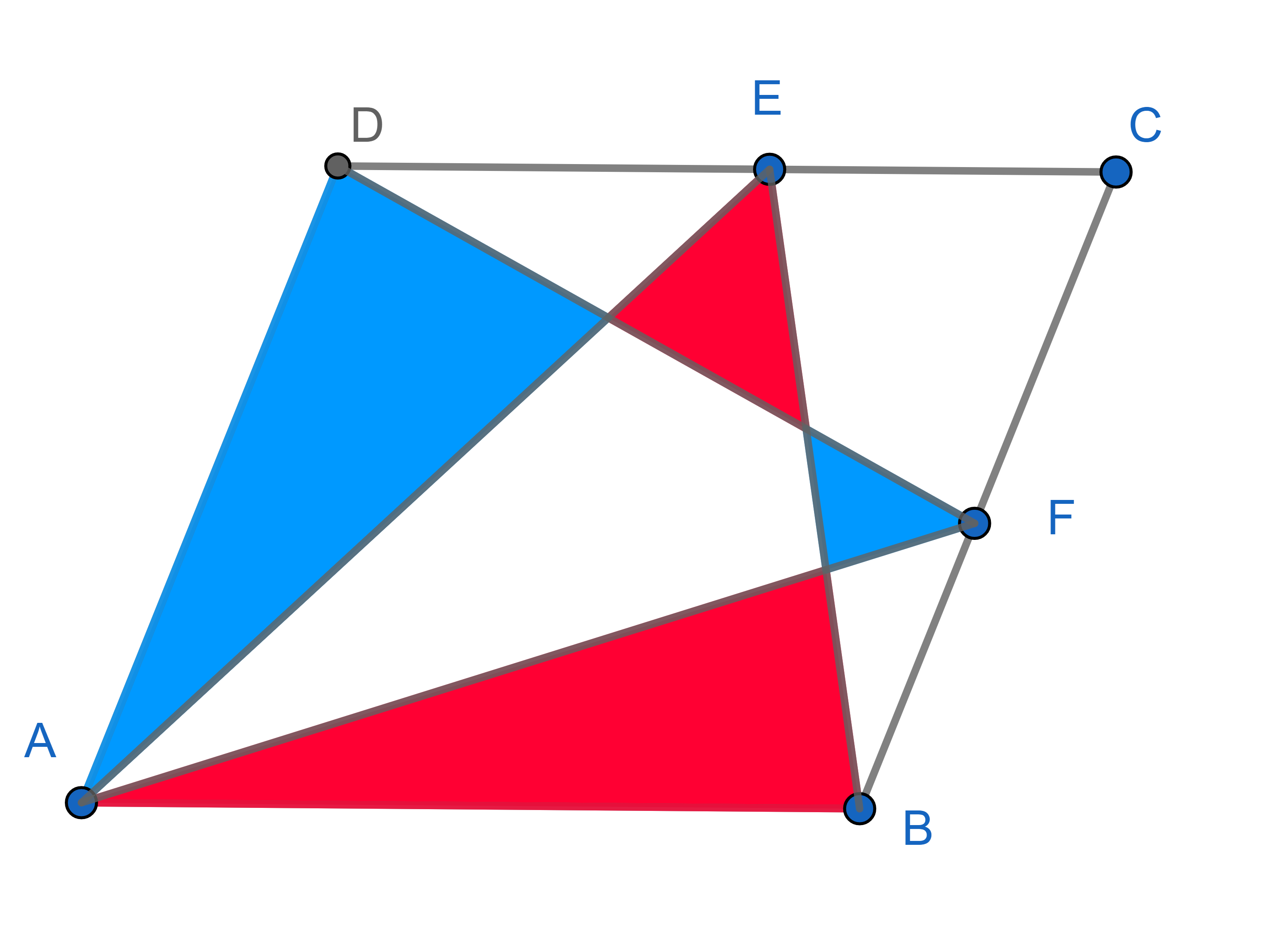
In a parallelogram \(ABCD\), point \(E\) belongs to the side \(CD\) and point \(F\) belongs to the side \(BC\). Show that the total red area is the same as the total blue area:
The figure below is a regular pentagram. What is larger, the black area or the blue area?

Among the first \(20\) Fibonacci numbers: \(F_0 = 0,F_1 = 1,F_2 = 1, F_3 = 2, F_4 = 3,..., F_{20} = 6765\) find all numbers whose digit-sum is equal to their index. For example, \(F_1=1\) fits the description, but \(F_{20} = 6765\) does not, since \(6+7+6+5 \neq 20\).
Among the first \(20\) Fibonacci numbers: \(F_0 = 0,F_1 = 1,F_2 = 1, F_3 = 2, F_4 = 3,..., F_{20} = 6765\) check whether the numbers with prime index are prime. The index is another name for a number’s place in the sequence.
