Problems
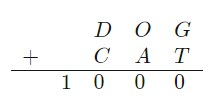
In the long addition above, each letter corresponds to a different digit. What is the sum \(D + O +G + C +A +T\)?
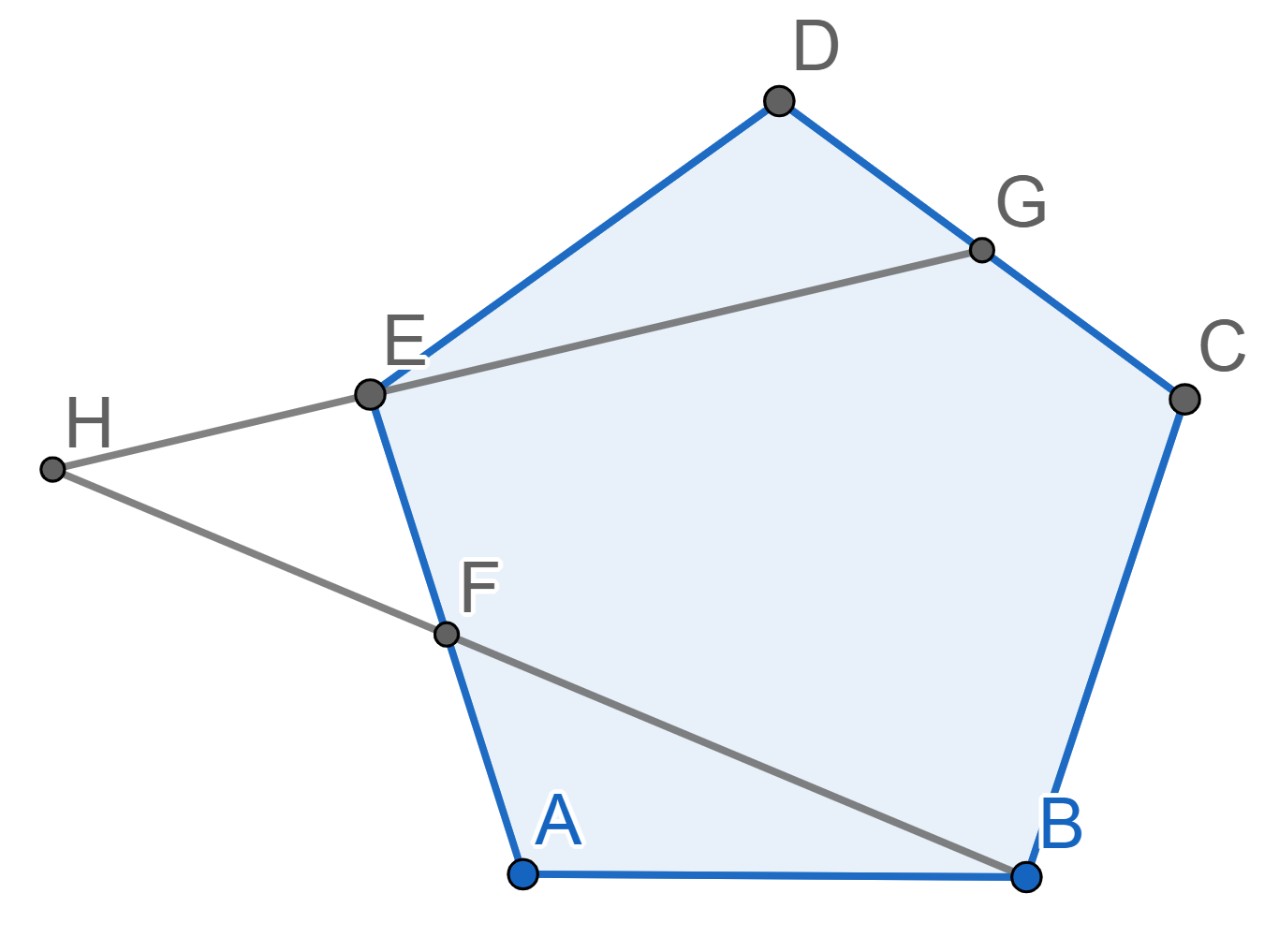
Let \(ABCDE\) be a regular pentagon. The point \(G\) is the midpoint of \(CD\), the point \(F\) is the midpoint of \(AE\). The lines \(EG\) and \(BF\) intersect at the point \(H\). Find the angle \(EHF\).
I have three positive integers. When you add them together, you get \(15\). When you multiply the three numbers together, you get \(120\).
What are the three numbers?
If a magician puts \(1\) dove into his hat, he pulls out \(2\) rabbits and \(2\) flowers from it. If the magician puts \(1\) rabbit in, he pulls out \(2\) flowers and \(2\) doves. If he puts \(1\) flower in, he pulls out \(1\) rabbit and \(3\) doves. The magician starts with \(1\) rabbit. Could he end up with the same number of rabbits, doves, and flowers after performing his hat trick several times?
In the other room there are two doors. The statements on them say:
There is treasure behind at least one of the doors.
There is treasure behind the first door.
Your guide says: The first sign is true if there is treasure behind the first door, otherwise it is false. The second sign is false if there is treasure behind the second door, otherwise it is true. What would you do?
For any real number \(x\), the absolute value of \(x\), written \(\left| x \right|\), is defined to be \(x\) if \(x>0\) and \(-x\) if \(x \leq 0\). What are \(\left| 3 \right|\), \(\left| -4.3 \right|\) and \(\left| 0 \right|\)?
Let \(x\) and \(y\) be real numbers. Prove that \(x \leq \left| x \right|\) and \(0 \leq \left| x \right|\). Then prove that the following inequality holds \(\left| x+y \right| \leq \left| x \right|+\left| y \right|\).
Is there a divisibility rule for \(2^n\), where \(n = 1\), \(2\), \(3\), . . .? If so, then explain why the rule works.
Can you find a formula relating \(1^3+2^3+\dots+n^3\) to \(1+2+\dots+n\)?
Prove the reverse triangle inequality: for every pair of real numbers \(x\), \(y\), we have \(\left| \left| x \right| - \left| y \right| \right| \leq \left| x - y \right|\).