Problems
In each cell of a board of size \(5\times5\) a cross or a nought is placed, and no three crosses are positioned in a row, either horizontally, vertically or diagonally. What is the largest number of crosses on the board?
An after school club is attended by 4 boys from class 7A, and four from class 7B. Of those who attended three were named Ben, three were named Will, and two were named Tom.
Is it possible for it to be the case that each boy had at least one namesake classmate who attended the club?
Authors: B. Vysokanov, N. Medved, V. Bragin
The teacher grades tests on a scale from 0 to 100. The school can change the upper bound of the scale to any other natural number, recalculating the estimates proportionally and rounding up to integers. A non-integer number, when rounded, changes to the nearest integer; if the fractional part is equal to 0.5, the direction of rounding can be either up or down and it can be different for each question. (For example, an estimate of 37 on a scale of 100 after recalculation in the scale of 40 will go to \(37 \cdot 40/100 = 14.8\) and will be rounded to 15).
The students of Peter and Valerie got marks, which are not 0 and 100. Prove that the school can do several conversions so that Peter’s mark becomes b and Valerie’s mark becomes a (both marks are recalculated simultaneously).
Author: A.A. Egorov
Calculate the square root of the number \(0.111 \dots 111\) (100 ones) to within a) 100; b) 101; c)* 200 decimal places.
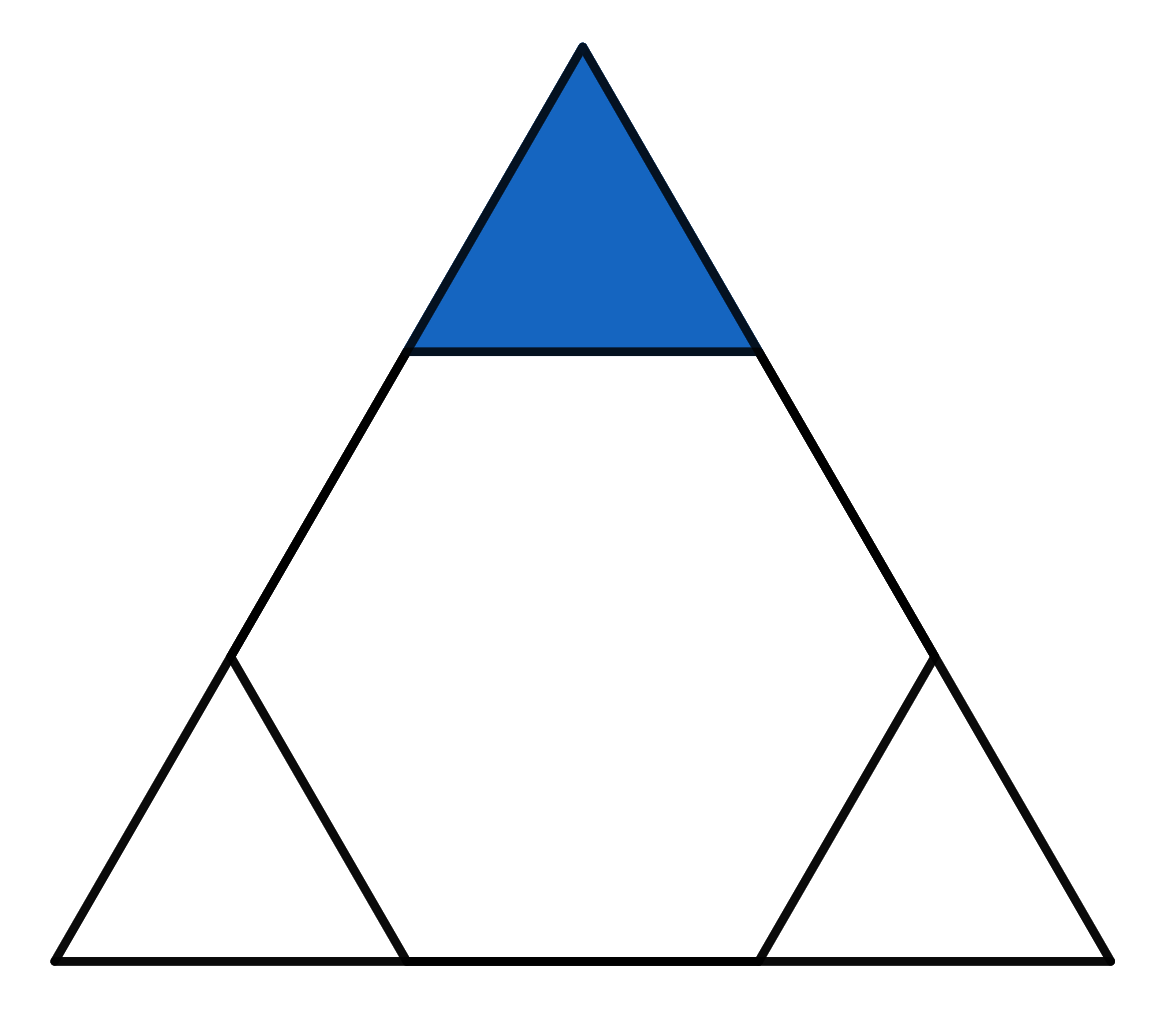
The triangle visible in the picture is equilateral. The hexagon inside is a regular hexagon. If the area of the whole big triangle is \(18\), find the area of the small blue triangle.
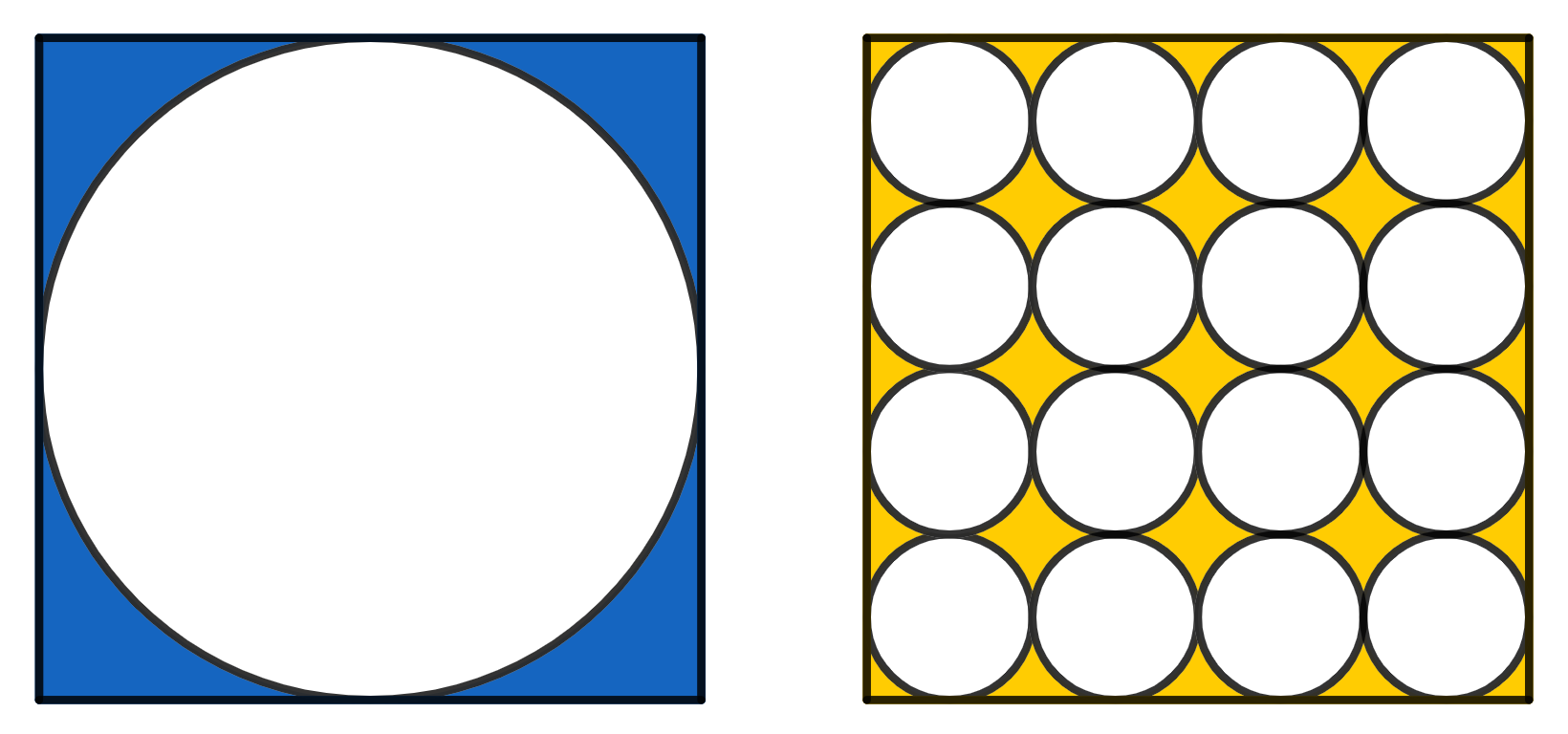
On the left there is a circle inscribed in a square of side 1. On the right there are 16 smaller, identical circles, which all together fit inside a square of side 1. Which area is greater, the yellow or the blue one?
Two people play a game with the following rules: one of them guesses a set of integers \((x_1, x_2, \dots , x_n)\) which are single-valued digits and can be either positive or negative. The second person is allowed to ask what is the sum \(a_1x_1 + \dots + a_nx_n\), where \((a_1, \dots ,a_n)\) is any set. What is the smallest number of questions for which the guesser recognizes the intended set?
Airlines connect pairs of cities. How can you connect 50 cities with the fewest number of airlines so that from every city you can get to any other city by taking at most two flights?
Two lines on the plane intersect at an angle \(\alpha\). On one of them there is a flea. Every second it jumps from one line to the other (the point of intersection is considered to belong to both straight lines). It is known that the length of each of her jumps is 1 and that she never returns to the place where she was a second ago. After some time, the flea returned to its original point. Prove that for the angle \(\alpha\) the value \(\alpha/\pi\) is a rational number.
The White Rook pursues a black horse on a board of \(3 \times 1969\) cells (they walk in turn according to the usual rules). How should the rook play in order to take the horse? White makes the first move.