Problems
A rectangular chocolate bar size \(5 \times 10\) is divided by vertical and horizontal division lines into 50 square pieces. Two players are playing the following game. The one who starts breaks the chocolate bar along some division line into two rectangular pieces and puts the resulting pieces on the table. Then players take turns doing the same operation: each time the player whose turn it is at the moment breaks one of the parts into two parts. The one who is the first to break off a square slice \(1\times 1\) (without division lines) a) loses; b) wins. Which of the players can secure a win: the one who starts or the other one?
What has a greater value: \(300!\) or \(100^{300}\)?
A quadrilateral is given; \(A\), \(B\), \(C\), \(D\) are the successive midpoints of its sides, \(P\) and \(Q\) are the midpoints of its diagonals. Prove that the triangle \(BCP\) is equal to the triangle \(ADQ\).
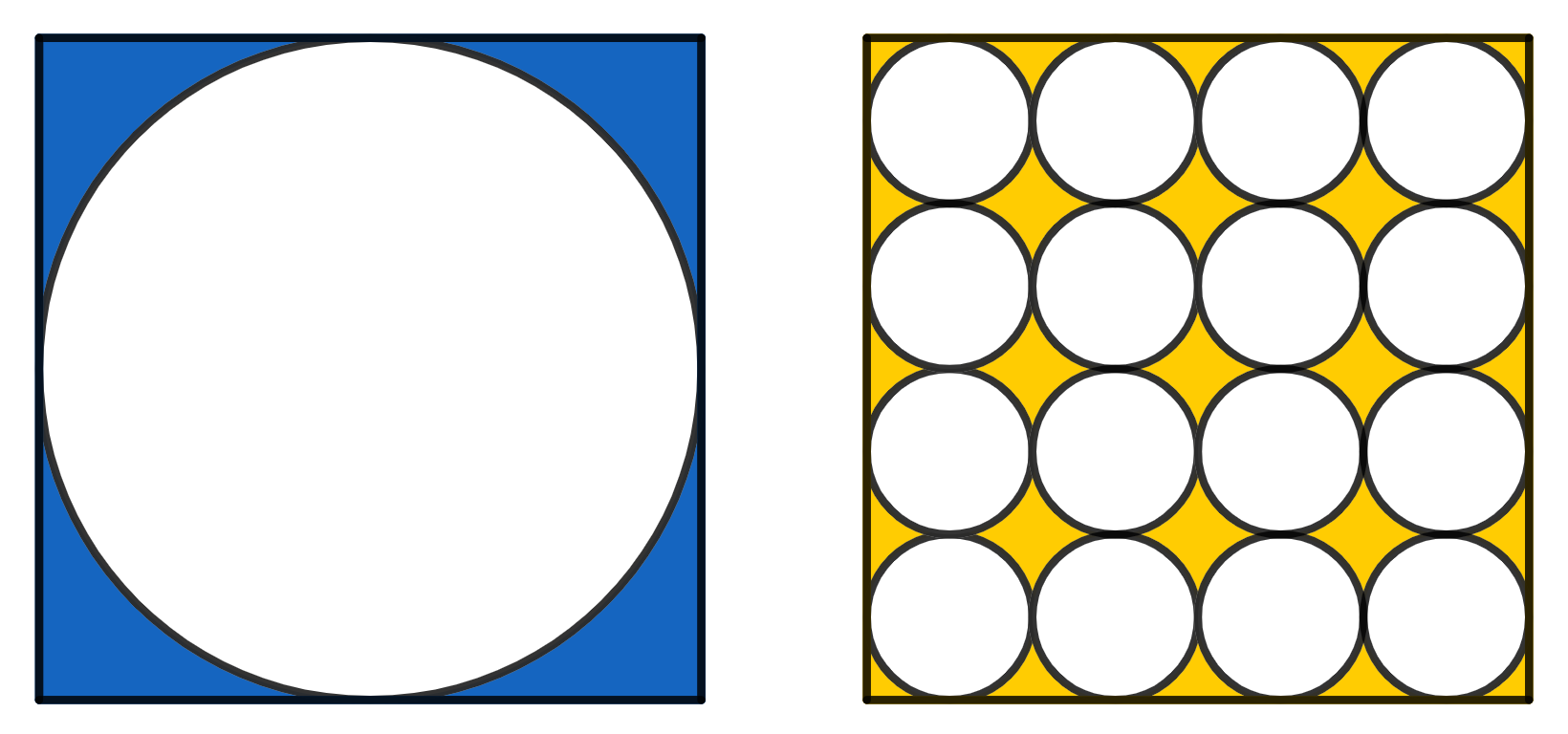
On the left there is a circle inscribed in a square of side 1. On the right there are 16 smaller, identical circles, which all together fit inside a square of side 1. Which area is greater, the yellow or the blue one?
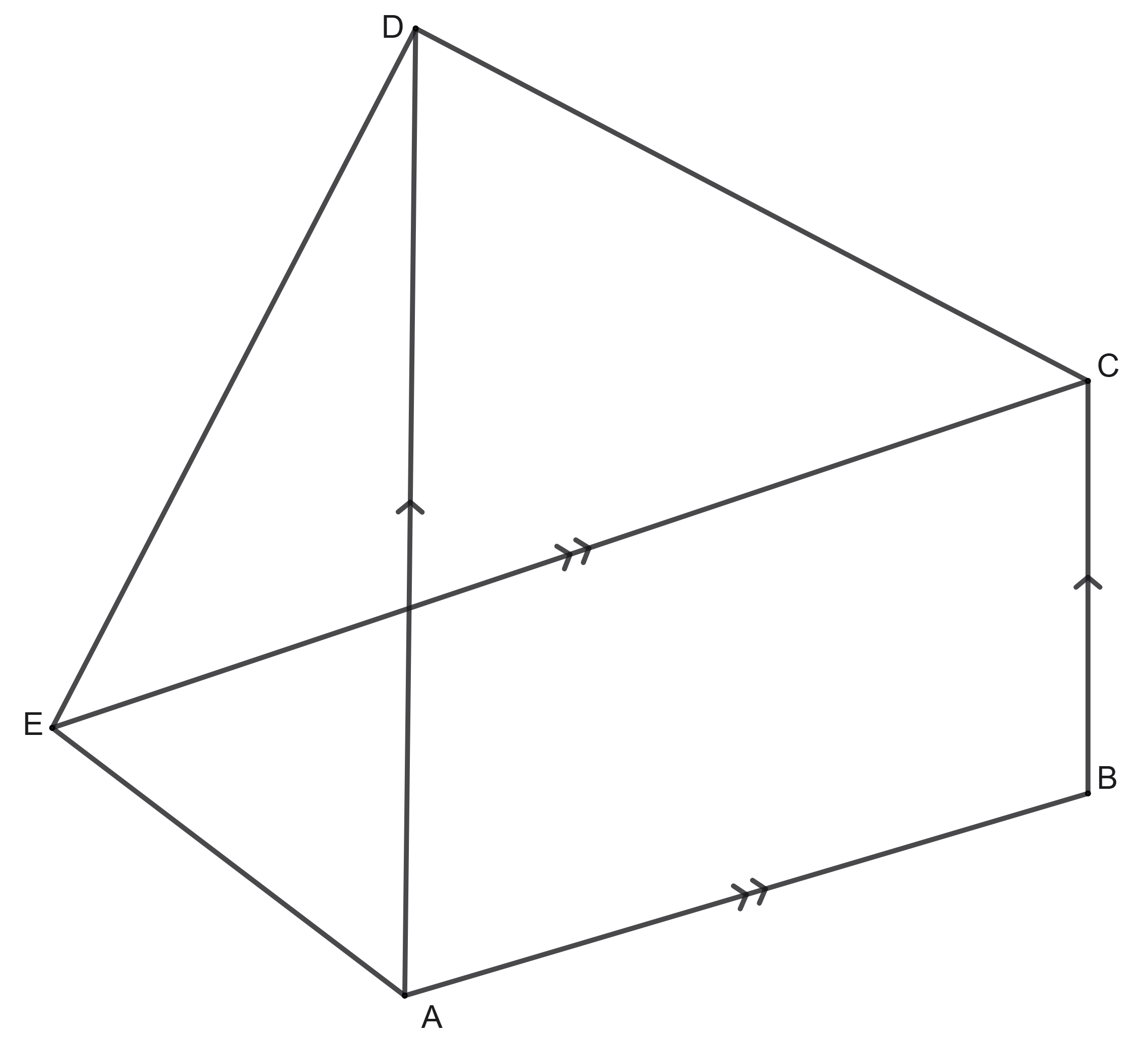
In a pentagon \(ABCDE\), diagonal \(AD\) is parallel to the side \(BC\) and the diagonal \(CE\) is parallel to the side \(AB\). Show that the areas of the triangles \(\triangle ABE\) and \(\triangle BCD\) are the same.
Prove that, for any integer \(n\), among the numbers \(n, n + 1, n + 2, \dots , n + 9\) there is at least one number that is mutually prime with the other nine numbers.
How can you arrange the numbers \(5/177\), \(51/19\) and \(95/9\) and the arithmetical operators “\(+\)”, “\(-\)”, “\(\times\)” and “\(\div\)” such that the result is equal to 2006? Note: you can use the given numbers and operators more than once.
There are 13 weights, each weighing an integer number of grams. It is known that any 12 of them can be divided into two cups of weights, six weights on each one, which will come to equilibrium. Prove that all the weights have the same weight.
If we are given any 100 whole numbers then amongst them it is always possible to choose one, or several of them, so that their sum gives a number divisible by 100. Prove that this is the case.
Numbers \(1, 2, 3, \dots , 101\) are written out in a row in some order. Prove that one can cross out 90 of them so that the remaining 11 will be arranged in their magnitude (either increasing or decreasing).