Problems
A target consists of a triangle divided by three families of parallel lines into 100 equilateral unit triangles. A sniper shoots at the target. He aims at a particular equilateral triangle and either hits it or hits one of the adjacent triangles that share a side with the one he was aiming for. He can see the results of his shots and can choose when to stop shooting. What is the largest number of triangles that the sniper can guarantee he can hit exactly 5 times?
Can the cells of a \(5 \times 5\) board be painted in 4 colours so that the cells located at the intersection of any two rows and any two columns are painted in at least three colours?
The real numbers \(x\) and \(y\) are such that for any distinct prime odd \(p\) and \(q\) the number \(x^p + y^q\) is rational. Prove that \(x\) and \(y\) are rational numbers.
Is it possible to arrange the numbers 1, 2, ..., 60 in a circle in such an order that the sum of every two numbers, between which lies one number, is divisible by 2, the sum of every two numbers between which lie two numbers, is divisible by 3, the sum of every two numbers between which lie six numbers, is divisible by 7?
The functions \(f (x) - x\) and \(f (x^2) - x^6\) are defined for all positive \(x\) and increase. Prove that the function
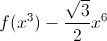
also increases for all positive \(x\).
The sum of the positive numbers \(a, b, c\) is \(\pi / 2\). Prove that \(\cos a + \cos b + \cos c > \sin a + \sin b + \sin c\).
The circles \(\sigma_1\) and \(\sigma_2\) intersect at points \(A\) and \(B\). At the point \(A\) to \(\sigma_1\) and \(\sigma_2\), respectively, the tangents \(l_1\) and \(l_2\) are drawn. The points \(T_1\) and \(T_2\) are chosen respectively on the circles \(\sigma_1\) and \(\sigma_2\) so that the angular measures of the arcs \(T_1A\) and \(AT_2\) are equal (the arc value of the circle is considered in the clockwise direction). The tangent \(t_1\) at the point \(T_1\) to the circle \(\sigma_1\) intersects \(l_2\) at the point \(M_1\). Similarly, the tangent \(t_2\) at the point \(T_2\) to the circle \(\sigma_2\) intersects \(l_1\) at the point \(M_2\). Prove that the midpoints of the segments \(M_1M_2\) are on the same line, independent of the positions of the points \(T_1, T_2\).
A set of weights has the following properties: It contains \(5\) weights, which are all different in weight. For any two weights, there are two other weights of the same total weight. What is the smallest number of weights that can be in this set?
Five teams participated in a football tournament. Each team had to play exactly one match with each of the other teams. Due to financial difficulties, the organisers cancelled some of the games. As a result, it turned out that all teams scored a different number of points and no team scored zero points. What is the smallest number of games that could be played in the tournament, if three points were awarded for a victory, one for a draw and zero for a defeat?
Natural numbers from 1 to 200 are divided into 50 sets. Prove that in one of the sets there are three numbers that are the lengths of the sides of a triangle.