Problems
On a line segment of length 1, \(n\) points are given. Prove that the sum of the distances from some point out of the ones on the segment to these points is no less than \(n / 2\).
Prove that in any triangle the sum of the lengths of the heights is less than the perimeter.
Prove that \(\angle ABC < \angle BAC\) if and only if \(AC < BC\), that is, the larger side lies opposite the larger angle of the triangle, and opposite the larger side lies the larger angle.
Prove that the area \(S_{ABC}\) of a triangle is equal to \(abc/4R\).
The point \(D\) lies on the base \(AC\) of the isosceles triangle \(ABC\). Prove that the radii of the circumscribed circles of the triangles \(ABD\) and \(CBD\) are equal.
Express the area of the triangle \(ABC\) through the length of the side \(BC\) and the angles \(B\) and \(C\).
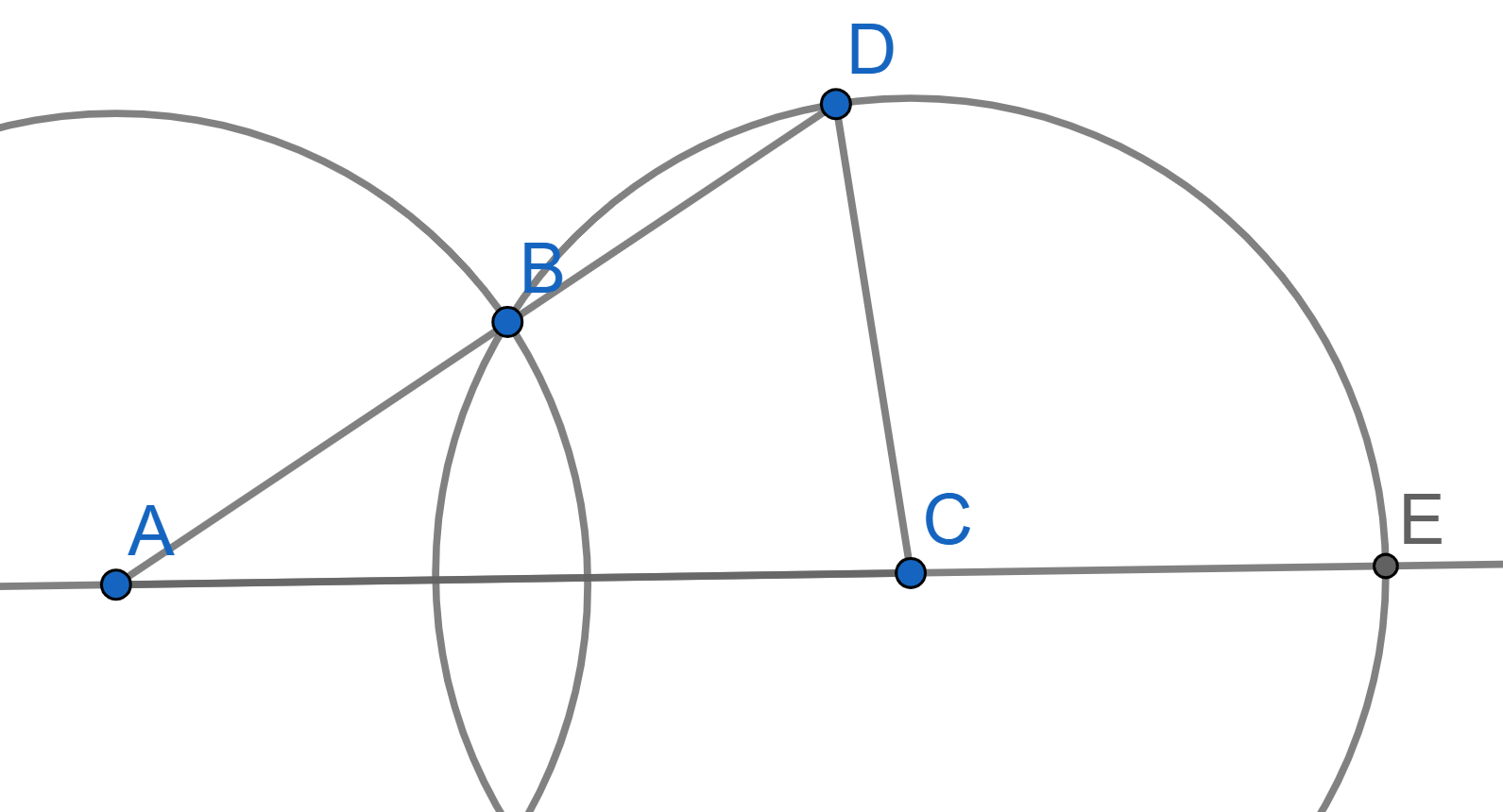
Two intersecting circles of radius \(R\) are given, and the distance between their centers is greater than \(R\). Prove that \(\angle ECD = 3\angle CAD\).
Find all triangles in which the angles form an arithmetic progression, and the sides form: a) an arithmetic progression; b) a geometric progression.
Prove that the point \(X\) lies on the line \(AB\) if and only if \(\overrightarrow{OX} = t \overrightarrow{OA} + (1 - t) \overrightarrow{OB}\) for some \(t\) and any point \(O\).
Several points are given and for some pairs \((A, B)\) of these points the vectors \(\overrightarrow{AB}\) are taken, and at each point the same number of vectors begin and end. Prove that the sum of all the chosen vectors is \(\vec{0}\).