Problems
At all rational points of the real line, integers are arranged. Prove that there is a segment such that the sum of the numbers at its ends does not exceed twice the number on its middle.
Prove that for any positive integer \(n\) the inequality
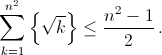
is true.
Find all the functions \(f\colon \mathbb {R} \rightarrow \mathbb {R}\) which satisfy the inequality \(f (x + y) + f (y + z) + f (z + x) \geq 3f (x + 2y + 3z)\) for all \(x, y, z\).
Find the sum \(1/3 + 2/3 + 2^2/3 + 2^3/3 + \dots + 2^{1000}/3\).
We are given a convex 200-sided polygon in which no three diagonals intersect at the same point. Each of the diagonals is coloured in one of 999 colours. Prove that there is some triangle inside the polygon whose sides lie some of the diagonals, so that all 3 sides are the same colour. The vertices of the triangle do not necessarily have to be the vertices of the polygon.
A number set \(M\) contains \(2003\) distinct positive numbers, such that for any three distinct elements \(a, b, c\) in \(M\), the number \(a^2 + bc\) is rational. Prove that we can choose a natural number \(n\) such that for any \(a\) in \(M\) the number \(a\sqrt{n}\) is rational.
A numeric set \(M\) containing 2003 distinct numbers is such that for every two distinct elements \(a, b\) in \(M\), the number \(a^2+ b\sqrt 2\) is rational. Prove that for any \(a\) in \(M\) the number \(q\sqrt 2\) is rational.
Is there a bounded function \(f\colon \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) such that \(f (1)> 0\) and \(f (x)\) satisfies the inequality \(f^2 (x + y) \geq f^2 (x) + 2f (xy) + f^2 (y)\) for all \(x, y \in \mathbb{R}\)?
Ten pairwise distinct non-zero numbers are such that for each two of them either the sum of these numbers or their product is a rational number.
Prove that the squares of all numbers are rational.
The polynomial \(P (x)\) of degree \(n\) has \(n\) distinct real roots.
What is the largest number of its coefficients that can be equal to zero?