Problems
In 25 boxes there are spheres of different colours. It is known that for any \(k\) where \(1 \leq k \leq 25\) in any \(k\) of the boxes there are spheres of exactly \(k+1\) different colours. Prove that a sphere of one particular colour lies in every single box.
The sequence \((a_n)\) is given by the conditions \(a_1 = 1000000\), \(a_{n + 1} = n \lfloor a_n/n\rfloor + n\). Prove that an infinite subsequence can be found within it, which is an arithmetic progression.
Given a square trinomial \(f (x) = x^2 + ax + b\). It is known that for any real \(x\) there exists a real number \(y\) such that \(f (y) = f (x) + y\). Find the greatest possible value of \(a\).
In the infinite sequence \((x_n)\), the first term \(x_1\) is a rational number greater than 1, and \(x_{n + 1} = x_n + \frac{1}{\lfloor x_n\rfloor }\) for all positive integers \(n\).
Prove that there is an integer in this sequence.
Note that in this problem, square brackets represent integers and curly brackets represent non-integer values or 0.
When water is drained from a pool, the water level \(h\) in it varies depending on the time \(t\) according to the function \(h (t) = at^2 + bt + c\), and at the time \(t_0\) of when the draining is ending, the equalities \(h (t_0) = h' (t_0) = 0\) are satisfied. For how many hours does the pool drain completely, if in the first hour the water level in it is reduced by half?
On the plane coordinate axes with the same but not stated scale and the graph of the function \(y = \sin x\), \(x\) \((0; \alpha)\) are given.
How can you construct a tangent to this graph at a given point using a compass and a ruler if: a) \(\alpha \in (\pi /2; \pi)\); b) \(\alpha \in (0; \pi /2)\)?
The sequence \(a_1, a_2, \dots\) is such that \(a_1 \in (1,2)\) and \(a_{k + 1} = a_k + \frac{k}{a_k}\) for any positive integer \(k\). Prove that it cannot contain more than one pair of terms with an integer sum.The sequence \(a_1, a_2, \dots\) is such that \(a_1 \in (1,2)\) and \(a_{k + 1} = a_k + \frac{k}{a_k}\) for any positive integer \(k\). Prove that it cannot contain more than one pair of terms with an integer sum.
Prove that if the expression
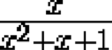
takes a rational value, then the expression
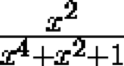
also takes on a rational value.
On an 8×8 grid (like a chessboard), an L-corner is a shape made of 3 little squares of the board that touch to make an L. You can turn the L any way you like. We place the L-corners so that none overlap. What is the fewest L-corners you must place so that no more L-corners can be added anywhere? Here is an example of how three L-corners may look like:
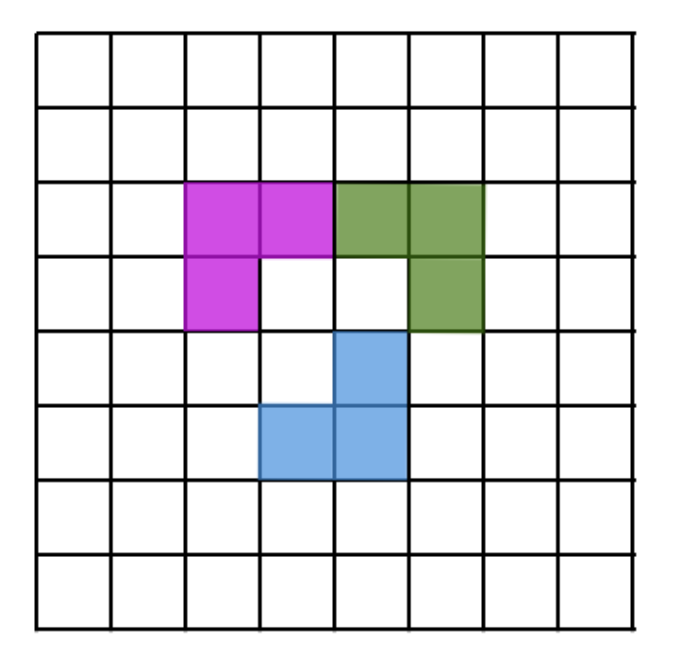
An airline flew exactly 10 flights each day over the course of 92 days. Each day, each plane flew no more than one flight. It is known that for any two days in this period there will be exactly one plane which flew on both those days. Prove that there is a plane that flew every day in this period.