Problems
Let’s denote any two digits with the letters \(A\) and \(X\). Prove that the six-digit number \(XAXAXA\) is divisible by 7 without a remainder.
A continuous function \(f(x)\) is such that for all real \(x\) the following inequality holds: \(f(x^2) - (f (x))^2 \geq 1/4\). Is it true that the function \(f(x)\) necessarily has an extreme point?
The numbers \(p\) and \(q\) are such that the parabolas \(y = - 2x^2\) and \(y = x^2 + px + q\) intersect at two points, bounding a certain figure.
Find the equation of the vertical line dividing the area of this figure in half.
The quadratic trinomials \(f (x)\) and \(g (x)\) are such that \(f' (x) g' (x) \geq | f (x) | + | g (x) |\) for all real \(x\). Prove that the product \(f (x) g (x)\) is equal to the square of some trinomial.
Given a square trinomial \(f (x) = x^2 + ax + b\). It is known that for any real \(x\) there exists a real number \(y\) such that \(f (y) = f (x) + y\). Find the greatest possible value of \(a\).
When water is drained from a pool, the water level \(h\) in it varies depending on the time \(t\) according to the function \(h (t) = at^2 + bt + c\), and at the time \(t_0\) of when the draining is ending, the equalities \(h (t_0) = h' (t_0) = 0\) are satisfied. For how many hours does the pool drain completely, if in the first hour the water level in it is reduced by half?
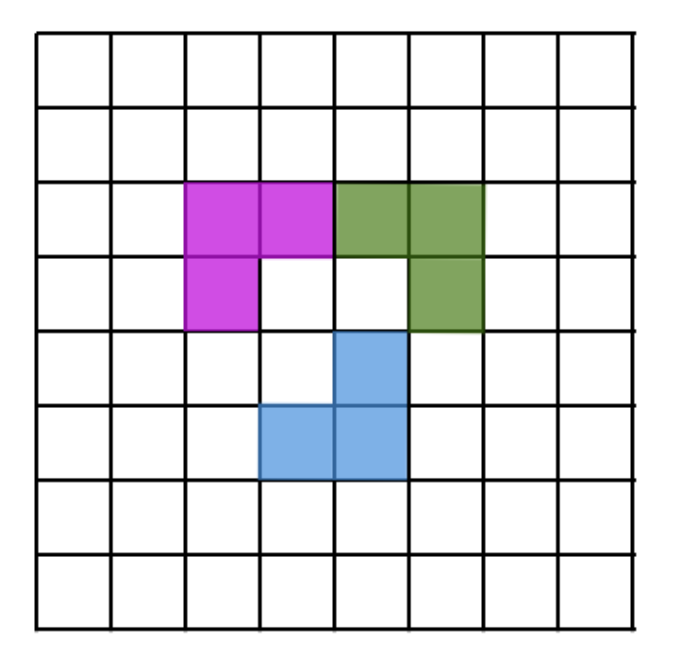
On an 8×8 grid (like a chessboard), an L-corner is a shape made of 3 little squares of the board that touch to make an L. You can turn the L any way you like. We place the L-corners so that none overlap. What is the fewest L-corners you must place so that no more L-corners can be added anywhere? Here is an example of how three L-corners may look like:
Prove that if the numbers \(x, y, z\) satisfy the following system of equations for some values of \(p\) and \(q\): \[\begin{aligned} y &= x^2 + px + q,\\ z &= y^2 + py + q,\\ x &= z^2 + pz + q, \end{aligned}\] then the inequality \(x^2y + y^2z + z^2x \geq x^2z + y^2x + z^2y\) is satisfied.
Three circles are constructed on a triangle, with the medians of the triangle forming the diameters of the circles. It is known that each pair of circles intersects. Let \(C_{1}\) be the point of intersection, further from the vertex \(C\), of the circles constructed from the medians \(AM_{1}\) and \(BM_{2}\). Points \(A_{1}\) and \(B_{1}\) are defined similarly. Prove that the lines \(AA_{1}\), \(BB_{1}\) and \(CC_{1}\) intersect at the same point.
Solve the following inequality: \(x+y^2 +\sqrt{x-y^2-1} \leq 1\).