Problems
Prove that for any positive integer \(n\) the inequality
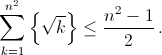
is true.
Find all the functions \(f\colon \mathbb {R} \rightarrow \mathbb {R}\) which satisfy the inequality \(f (x + y) + f (y + z) + f (z + x) \geq 3f (x + 2y + 3z)\) for all \(x, y, z\).
Find the sum \(1/3 + 2/3 + 2^2/3 + 2^3/3 + \dots + 2^{1000}/3\).
We are given a convex 200-sided polygon in which no three diagonals intersect at the same point. Each of the diagonals is coloured in one of 999 colours. Prove that there is some triangle inside the polygon whose sides lie some of the diagonals, so that all 3 sides are the same colour. The vertices of the triangle do not necessarily have to be the vertices of the polygon.
Is it possible to arrange natural numbers from 1 to \(2002^2\) in the cells of a \(2002\times2002\) table so that for each cell of this table one could choose a triplet of numbers, from a row or column, where one of the numbers is equal to the product of the other two?
A number set \(M\) contains \(2003\) distinct positive numbers, such that for any three distinct elements \(a, b, c\) in \(M\), the number \(a^2 + bc\) is rational. Prove that we can choose a natural number \(n\) such that for any \(a\) in \(M\) the number \(a\sqrt{n}\) is rational.
A numeric set \(M\) containing 2003 distinct numbers is such that for every two distinct elements \(a, b\) in \(M\), the number \(a^2+ b\sqrt 2\) is rational. Prove that for any \(a\) in \(M\) the number \(q\sqrt 2\) is rational.
Is there a bounded function \(f\colon \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) such that \(f (1)> 0\) and \(f (x)\) satisfies the inequality \(f^2 (x + y) \geq f^2 (x) + 2f (xy) + f^2 (y)\) for all \(x, y \in \mathbb{R}\)?
For which \(\alpha\) does there exist a function \(f\colon \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) that is not a constant, such that \(f (\alpha (x + y)) = f (x) + f (y)\)?
We are given a table of size \(n \times n\). \(n-1\) of the cells in the table contain the number \(1\). The remainder contain the number \(0\). We are allowed to carry out the following operation on the table:
1. Pick a cell.
2. Subtract 1 from the number in that cell.
3. Add 1 to every other cell in the same row or column as the chosen cell.
Is it possible, using only this operation, to create a table in which all the cells contain the same number?