Problems
On a circle of radius 1, the point \(O\) is marked and from this point, to the right, a notch is marked using a compass of radius \(l\). From the obtained notch \(O_1\), a new notch is marked, in the same direction with the same radius and this is process is repeated 1968 times. After this, the circle is cut at all 1968 notches, and we get 1968 arcs. How many different lengths of arcs can this result in?
In a regular polygon with \(25\) vertices, all the diagonals are drawn.
Prove that there are no nine diagonals passing through one interior point of the shape.
Point \(A\) is the centre of a circle and points \(B,C,D\) lie on that circle. The segment \(BD\) is a diameter of the circle. Show that \(\angle CAD = 2 \angle CBD\). This is a special case of the inscribed angle theorem.
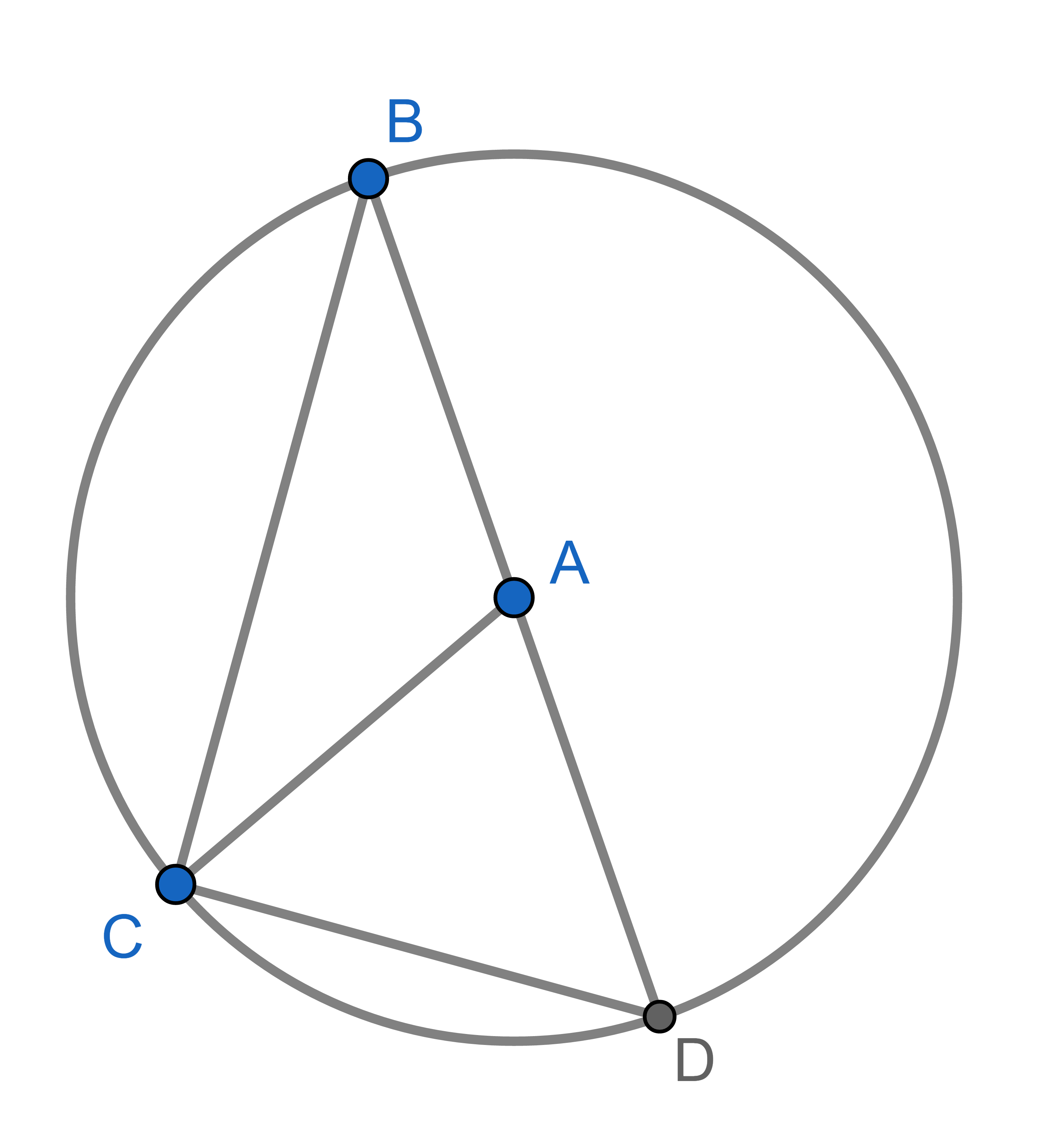
Point \(A\) is the centre of a circle and points \(B,C,D\) lie on that circle. Show that \(\angle CAD = 2 \angle CBD\). This statement is known as the inscribed angle theorem and is used widely in Euclidean geometry.
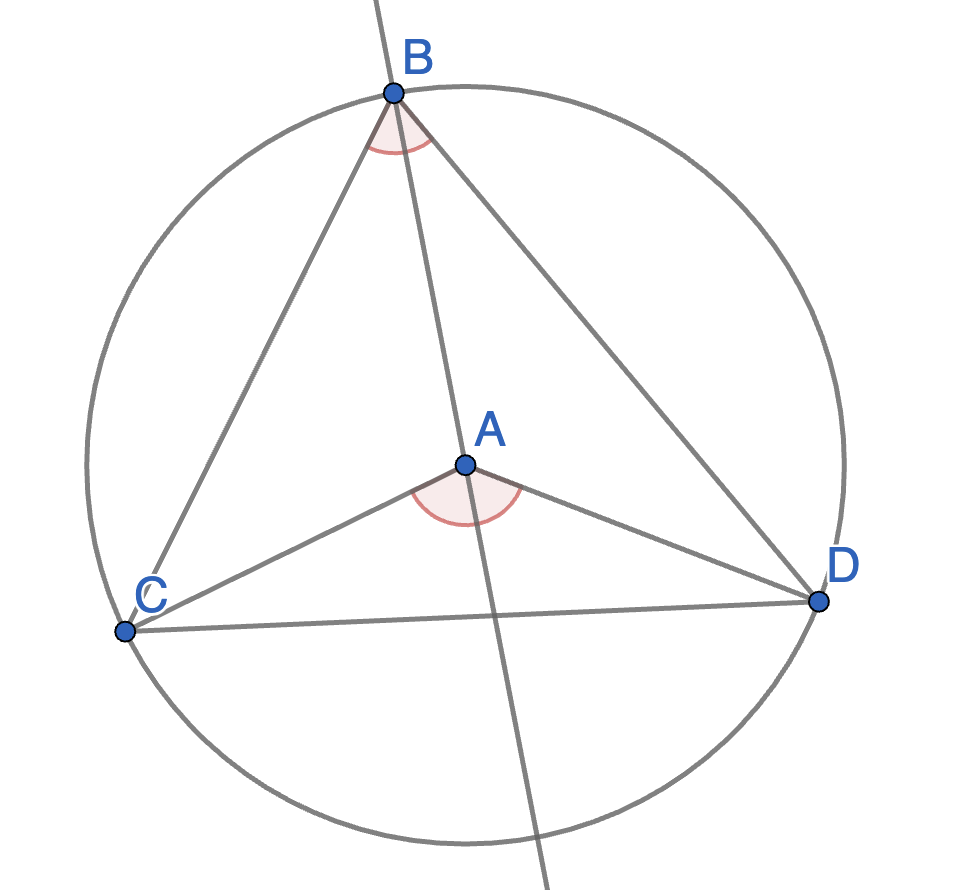
Let \(BCDE\) be a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle with centre \(A\). Show that angles \(\angle CDE\) and \(\angle CBE\) are equal. Also show that angles \(\angle BCD\) and \(\angle BED\) are equal. This says that all angles at the circumference subtended by the same arc are equal.
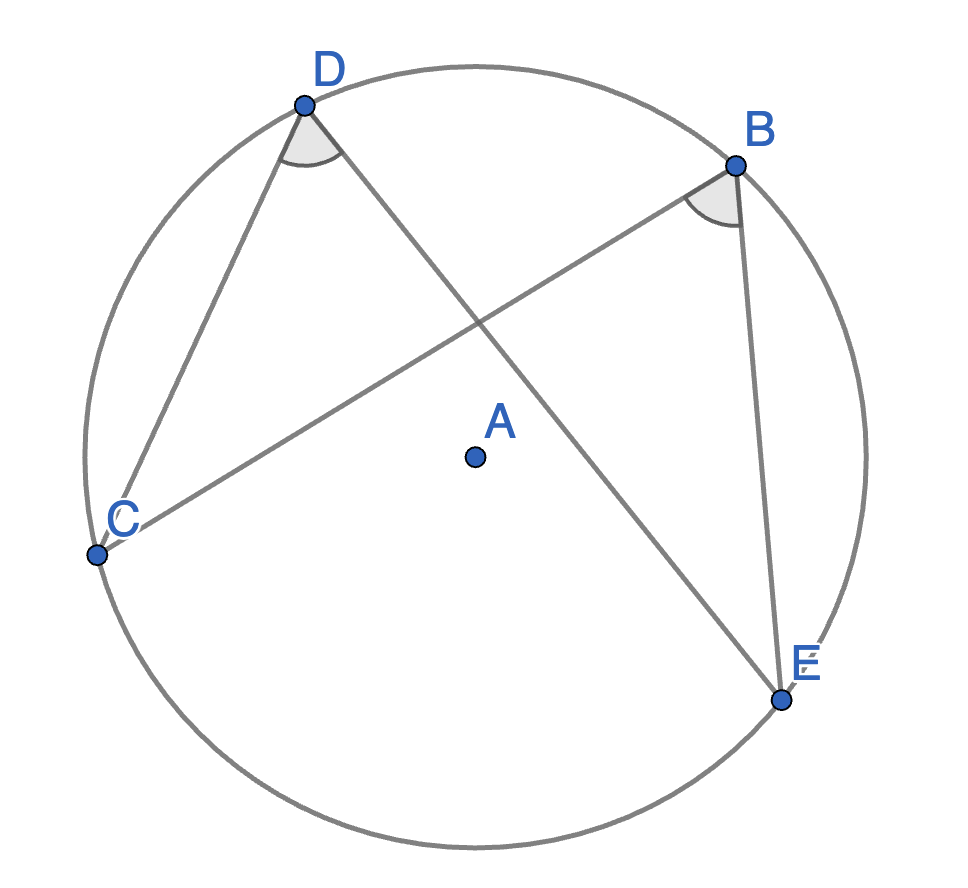
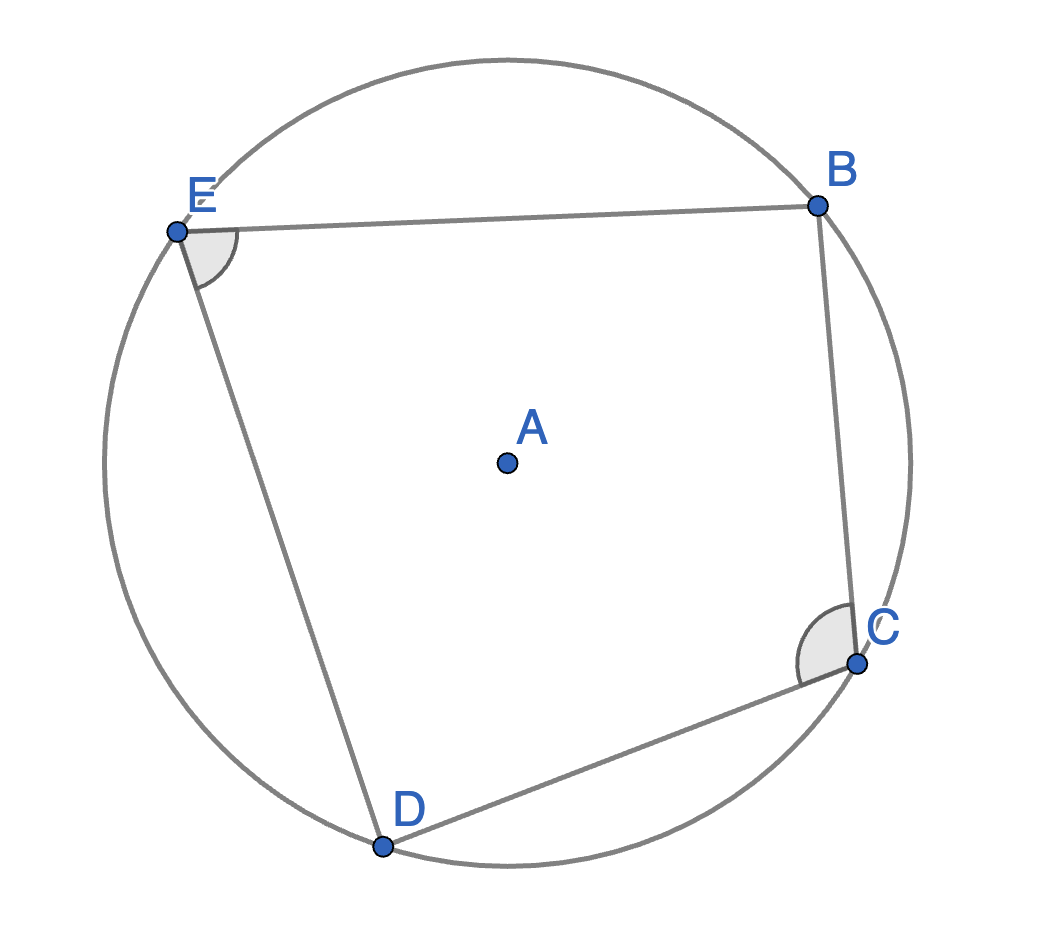
Let \(BCDE\) be an inscribed quadrilateral. Show that \(\angle BCD + \angle BED = 180^{\circ}\).
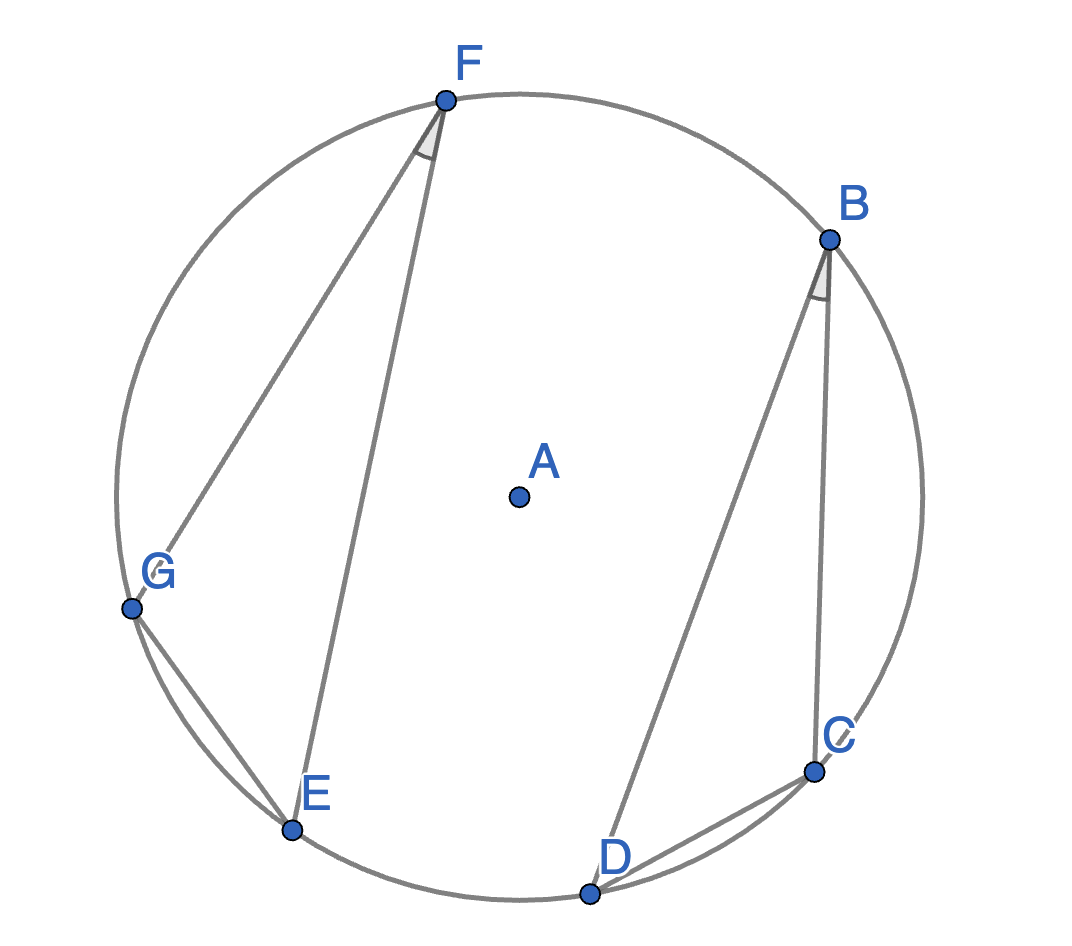
The points \(B\),\(C\),\(D\),\(E\),\(F\) and \(G\) lie on a circle with centre \(A\). The angles \(\angle CBD\) and \(\angle EFG\) are equal. Prove that the segments \(CD\) and \(EG\) have equal lengths.
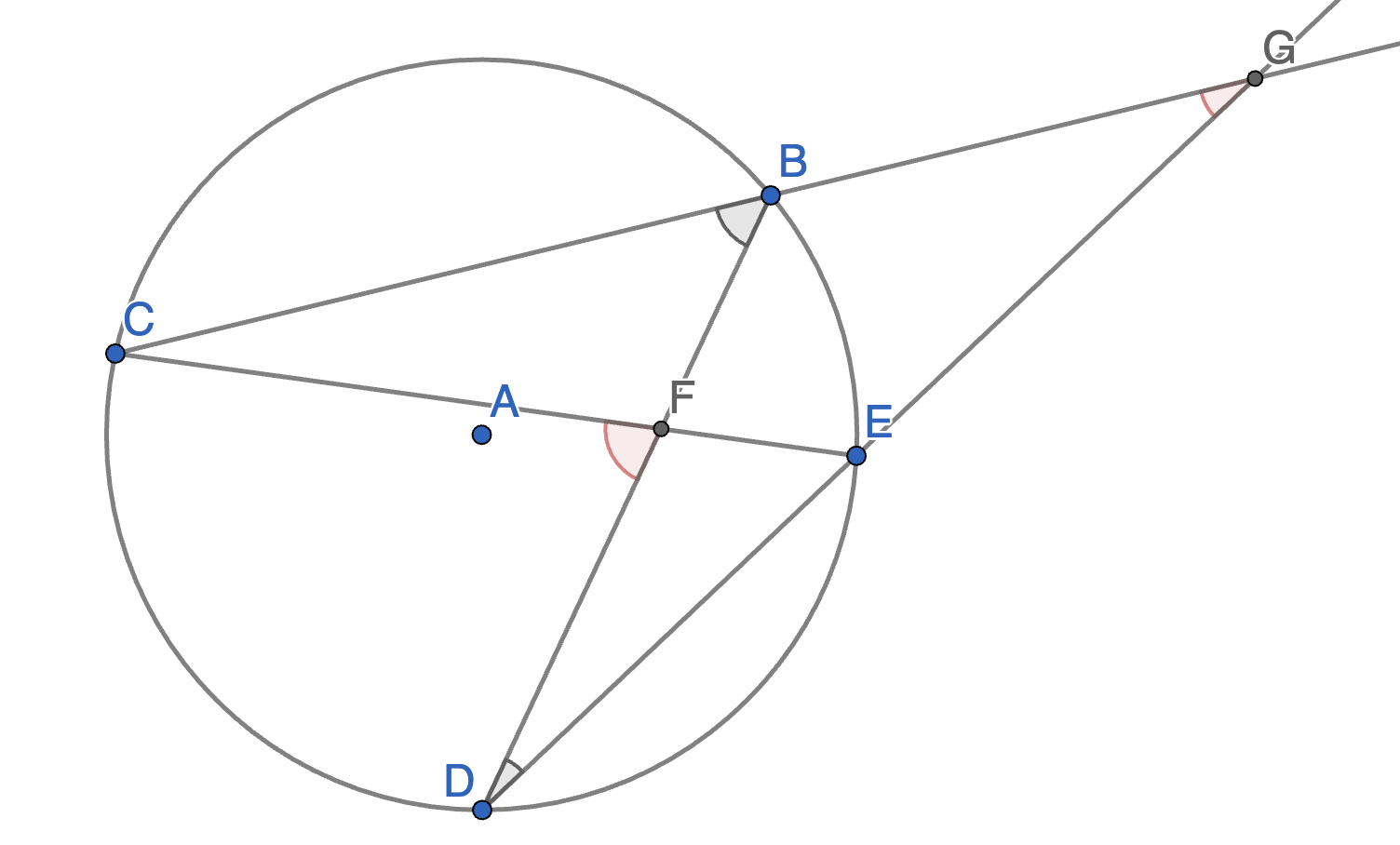
On the diagram below find the value of the angles \(\angle CFD\) and \(\angle CGD\) in terms of angles \(\angle CBD\) and \(\angle BDE\).
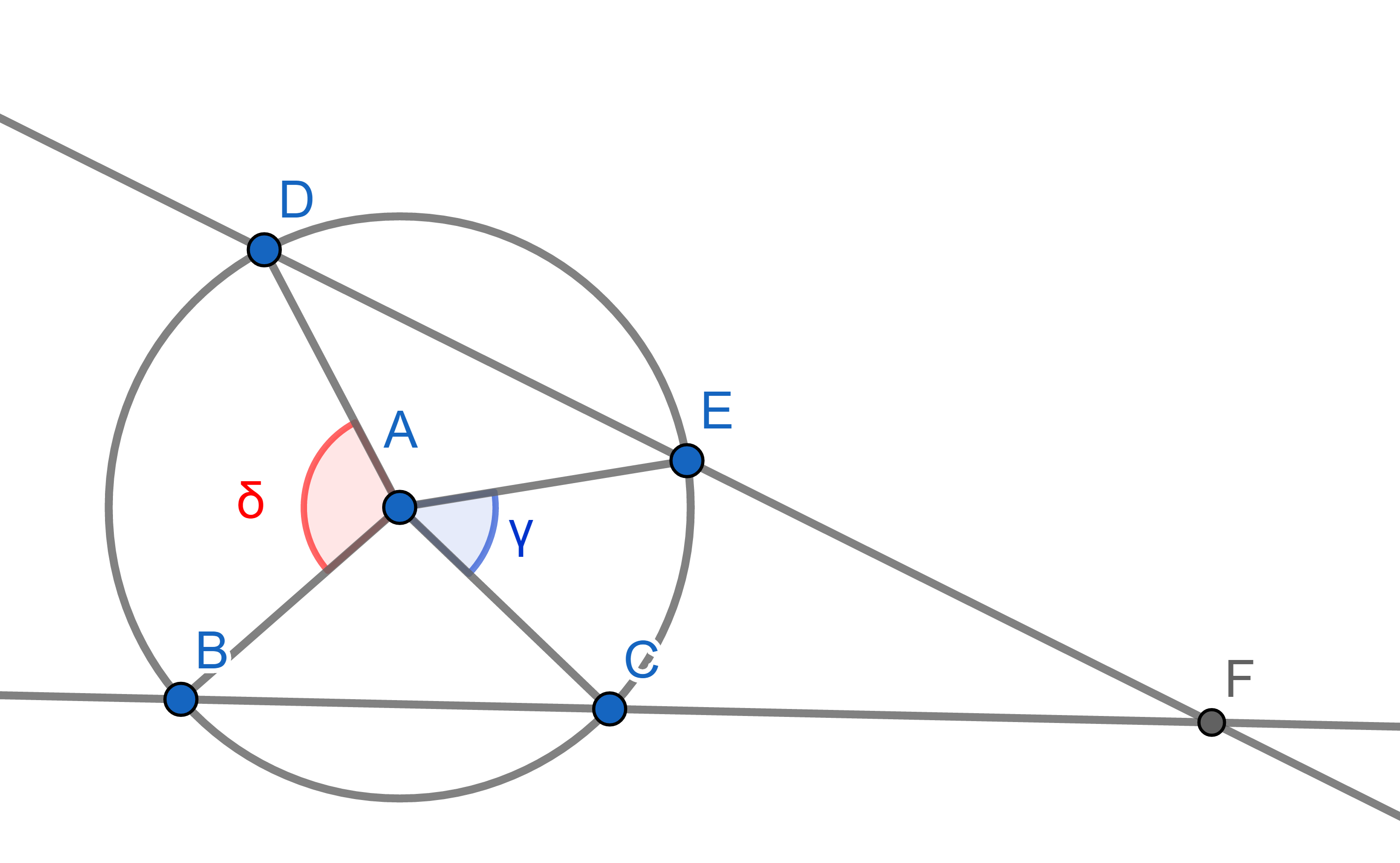
Point \(A\) is the centre of a circle. Points \(B,C,D,E\) lie on the circumference of this circle. Lines \(BC\) and \(DE\) cross at \(F\). We label the angles \(\angle BAD =\delta\) and \(\angle CAE = \gamma\). Express the angle \(DFB\) in terms of \(\gamma\) and \(\delta\).
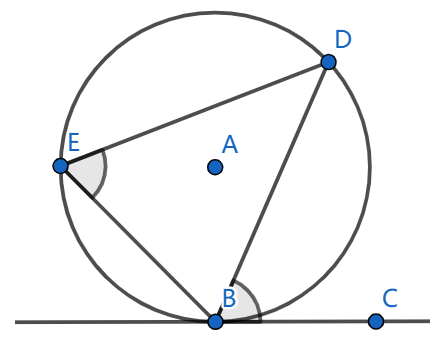
On the diagram below \(BC\) is the tangent line to a circle with the centre \(A\), and it is known that the angle \(\angle ABC = 90^{\circ}\). Prove that the angles \(\angle DEB\) and \(\angle DBC\) are equal.